21 Plant Morphology
Plant morphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants
Most of the plants you are familiar with are put together in a similar way.
You will learn more about this throughout the unit.
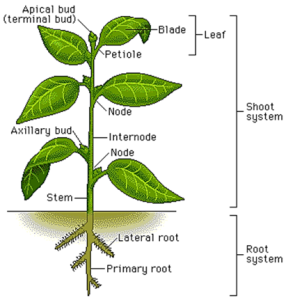

Plant form is the shape in which the plant grows.
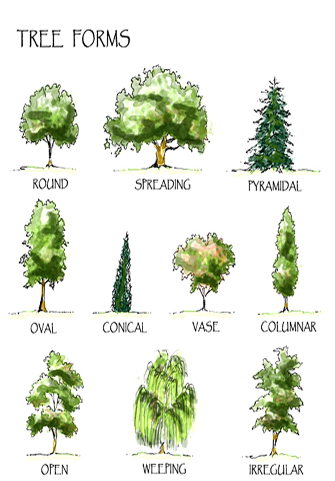
Each plant habit can have different forms. For example, consider these various forms:
Tree Forms
Shrub Forms
- Mounded
- Rounded
- Prostrate
- Upright
- Straggly
- Horizontal
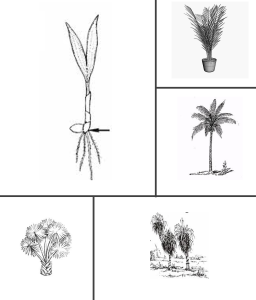
Palm Forms
Palm or palm-like habit includes cycads and plants such as Pandanus which are common plants in Northern Australia. They include:
- Single stemmed
- Multi stemmed
- Rosette forming
- Spiralling
Grass Forms
Grasses are very familiar to us in our everyday lives. Think of the grasses you are familiar with.
What grasses do you already know?
- Lemon grass, couch (a lawn grass)
- Tussock
- Matt forming
Climber Forms

Active mechanisms
Passive mechanisms

