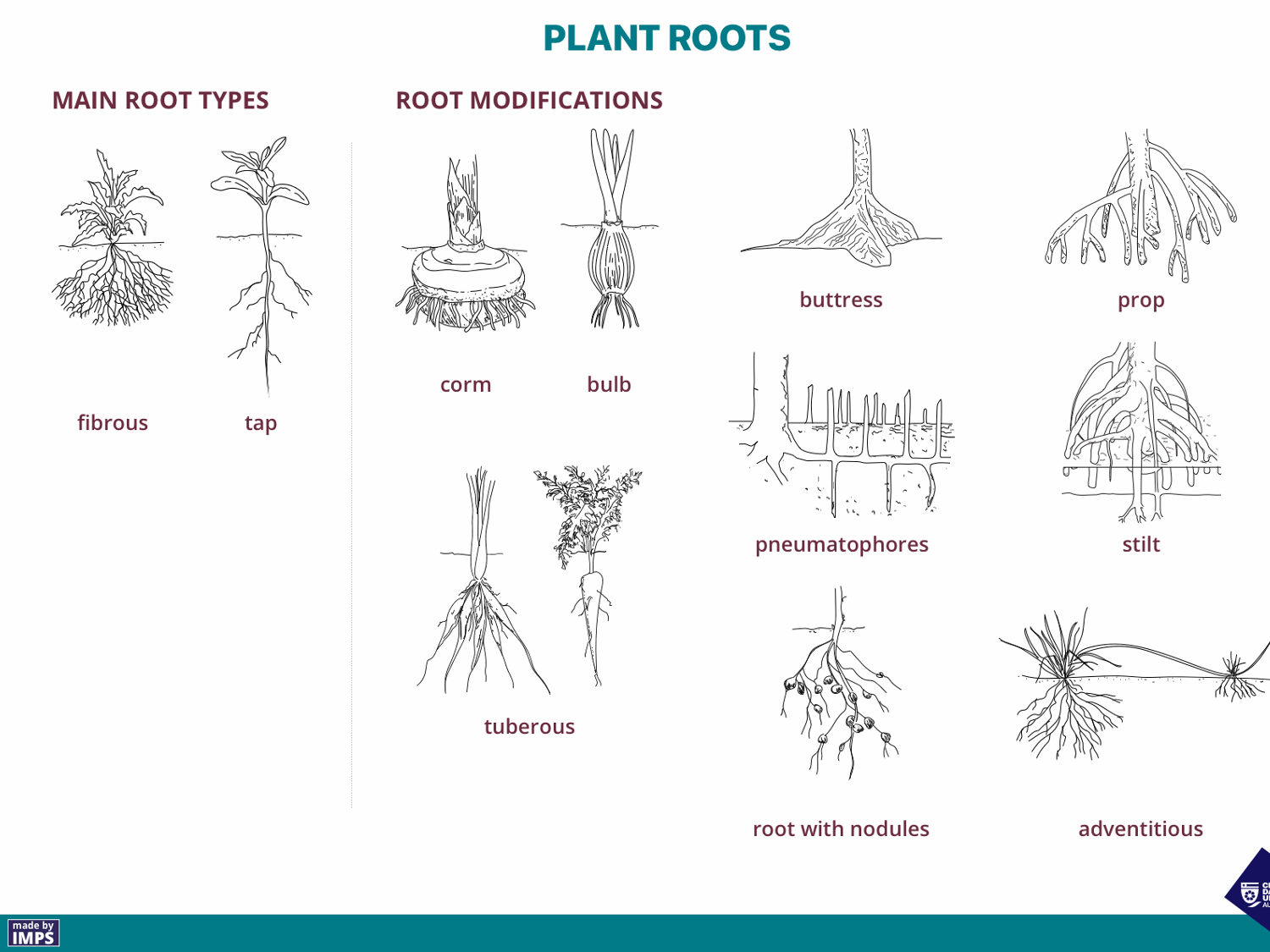
23 Root Modifications
Roots can be modified for survival.
Roots which survive the winter contain food material (e.g., starch) which will be used by the developing shoots in spring. Man has made use of such stores in plants like carrots, turnips, and beetroot.
- Adventitious roots– arising all the way along the stem on plants such as ivy, Ficus pumila are– as also the roots on strawberry runners. Some tropical orchids which grow on tree-trunks have spongy roots exposed to the air. The roots absorb moisture and may contain chlorophyll too.
- Stilt roots which develop from nodes on the stem and provide extra support, some common plant which have stilt roots are Corn, sugar cane, Pandanus plants and many others.
- Prop roots are a modified root used by the banyan tree, and other Ficuses’, the roots develop in the horizontal branches and grow into the soil. They form solid supports for the spreading branches.
- Pneumatophores or respiratory roots are found in plant growing in mangroves or swamps near the sea-shore. Pneumatophores arise vertically upwards and come out of soil and water. They bear small pores called pneumatothodes or lenticels for exchange of gases, e.g. Mangroves due to the swampy soil being poor in oxygen.
- Nodulated roots -bearing small nodule like swellings. The root nodules contain nitrogen fixing bacteria, these bacteria convert free atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds of nitrogen and the process is called nitrogen fixation. These plants increase the fertility of soil by adding nitrates, e.g. Leguminous plants (often used in green manures and as part of crop rotation.(pea and other legumes)