1.6 Chloroplasts
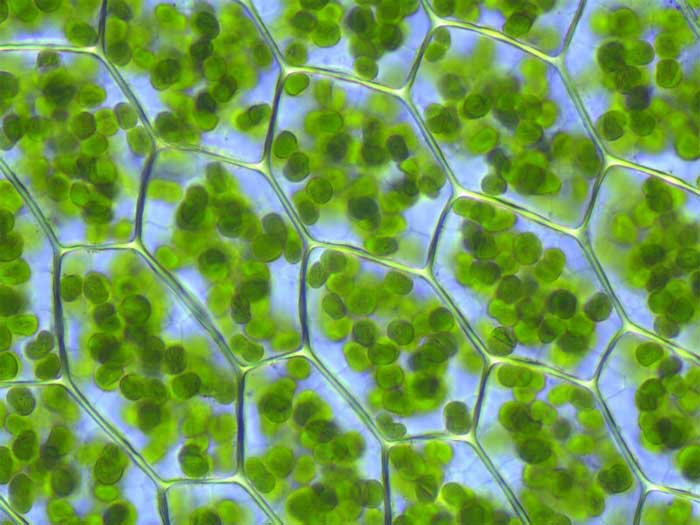
Chloroplasts are large organelles and their function is the formation and storage of carbohydrates from photosynthesis. The chloroplast is bounded by a double membrane.
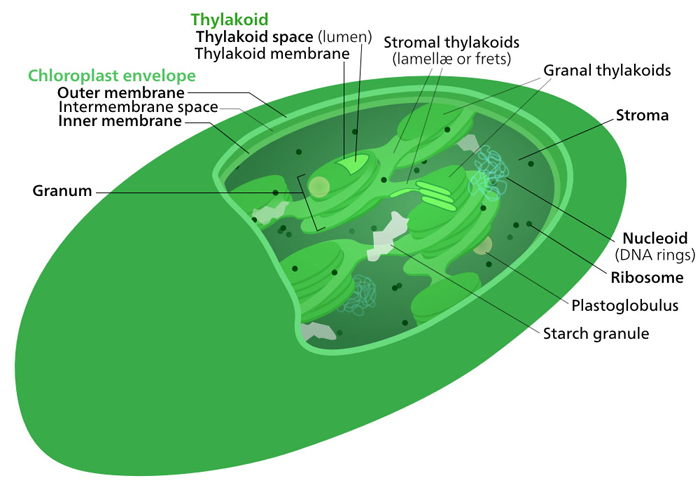
The matrix of the chloroplast is known as the stroma. Also inside the chloroplast are separate internal membranes that form lamellae or rounded tongue-like thylakoids within the enclosing double membrane. These tongue-like or disk-like thylakoid membranes may be stacked in layers and these are referred to as grana. Grana are joined to each other by other membranes.
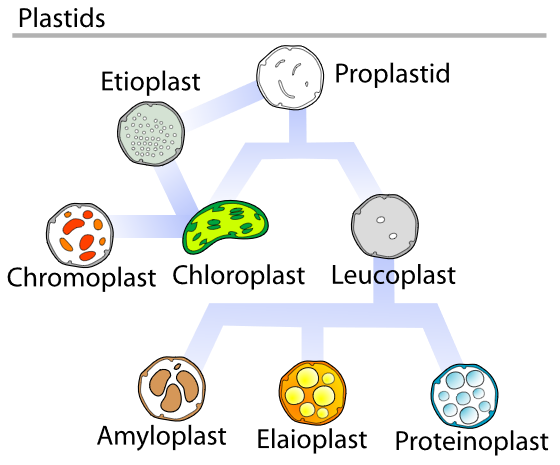
There are a range of other organelles which are similar to chloroplasts that are used for storage and pigmentation.
Media Attributions
- Figure 1.14. Chloroplasts in the leaf cell of a moss, Plagiomnium affine. © Kristian Peters is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 1.15. Internal membrane structure of a chloroplast within a chloroplast © Kelvinsong is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 1.16. Other plastids in a plant cell © Mariana Ruiz Villarreal adapted by Kelvinsong is licensed under a Public Domain license

