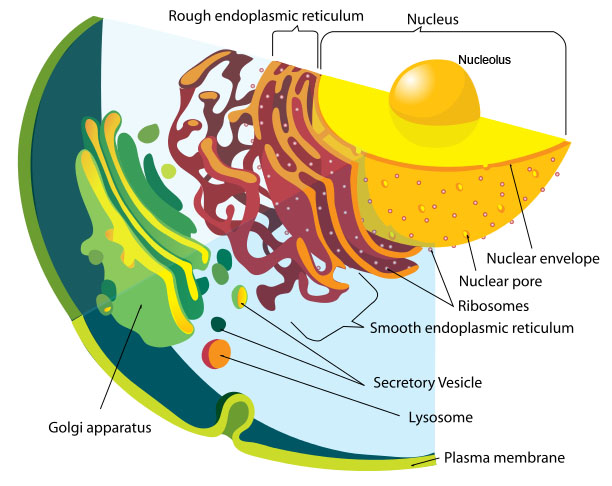
1.4 The nucleus
The nucleus is the control centre of the cell and is often the largest organelle in the cell. It contains about 20% ribonucleic acid (RNA) and 20% deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). It has four parts: nuclear envelope (membrane), nucleoplasm, nucleolus and chromosomes or chromatin.
The nuclear envelope is a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus. It contains pores that allow rapid communication between the cytoplasm of the cell and the nucleoplasm.
Nucleoplasm is similar to the cytoplasm of the cell but contains more protein macromolecules and appears darker than the cytoplasm.
The nucleolus is a roughly spherical body consisting of a mass of fine threads and particles of RNA, proteins and DNA. Its major role is the synthesis of ribosomal RNA.