2.2 Ground tissues
The main tissue types of the ground tissue system are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Parenchyma have thin walls of cellulose, whereas collenchyma have cell walls with thickened areas of additional cellulose. Sclerenchyma cells have lignified cell walls. They can be further categorised into narrow long cells (fibers) and cells of various other shapes (sclereids).
2.2.1 Parenchyma
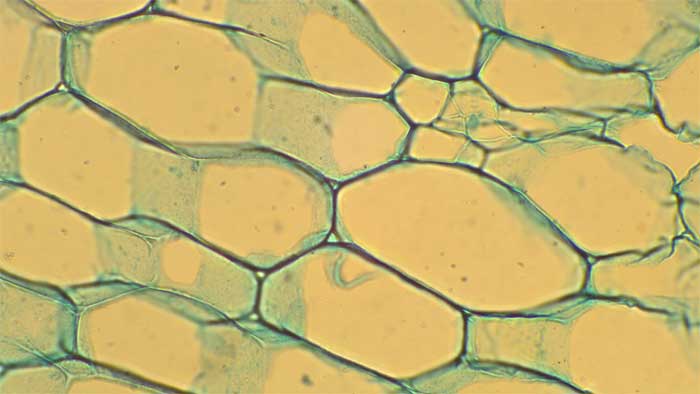
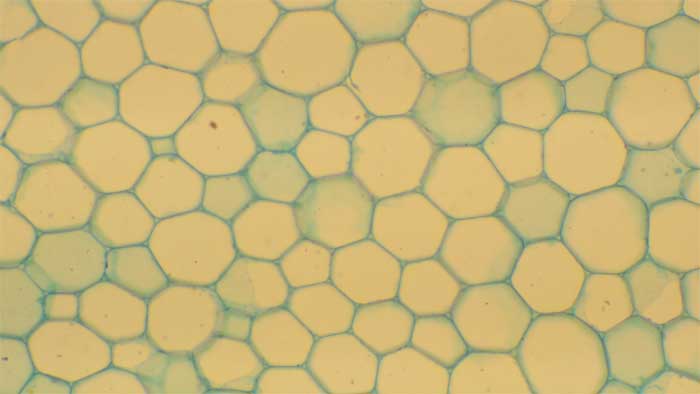
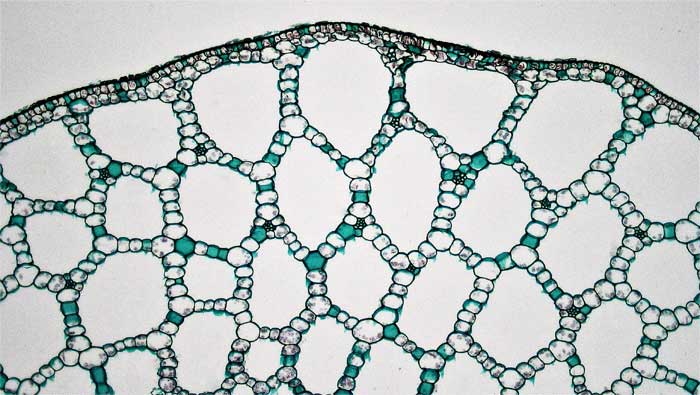
When parenchyma cells are modified to create tissues with air spaces for buoyancy or aeration of tissues, then the tissue is described as aerenchyma rather than parenchyma.
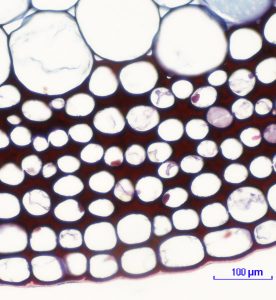
2.2.2 Collenchyma
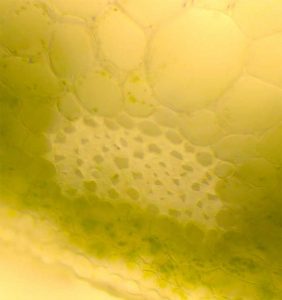
2.2.3 Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma cells have lignified cell walls. They can be of two broad types: sclereids and fiber cells.
2.2.3.1 Sclereids
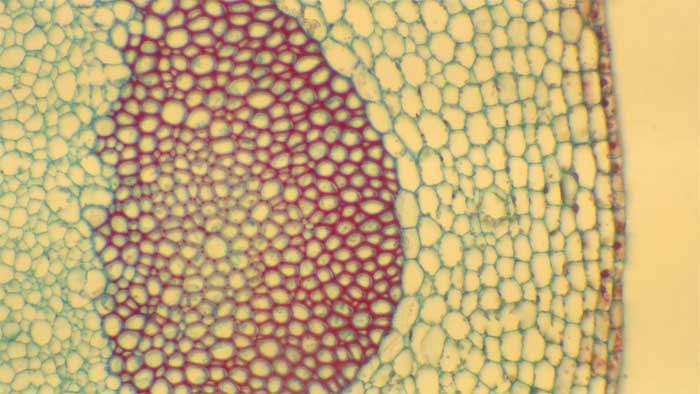
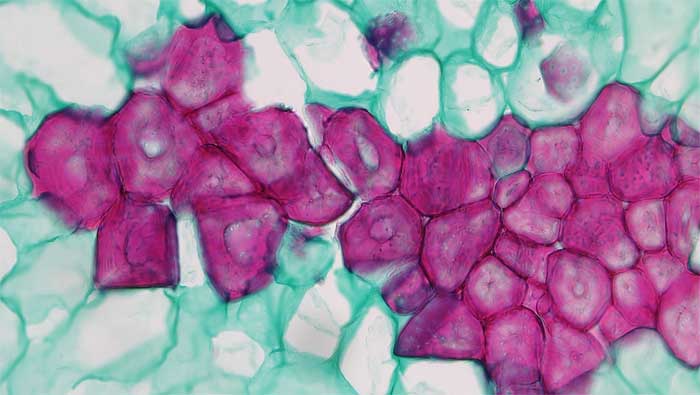
2.2.3.2 Fibers
Fiber cells are sclerenchyma cells that are long and thin.
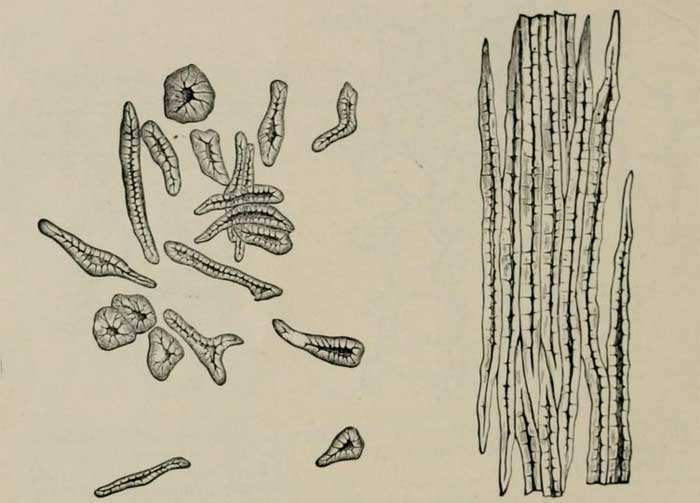
Media Attributions
- Figure 2.3.a. Parenchyma cells with blue green thin cellulose cell walls © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.3.b. Parenchyma cells with blue green thin cellulose cell walls © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.4. Aerenchyma in the stem of the aquatic monocot Potamogeton © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.5.a. Fraxinus collenchyma © Jen Dixon is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.5.b. Collenchyma cells in celery © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.6.a. Sclerenchyma cells © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.6.b. Sclereid cells or stone cells in the pear fruit © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.7. Drawings of sclerenchyma and fibers © Winton, A.L., Moeller, J., & Winton, K.G.B is licensed under a Public Domain license

