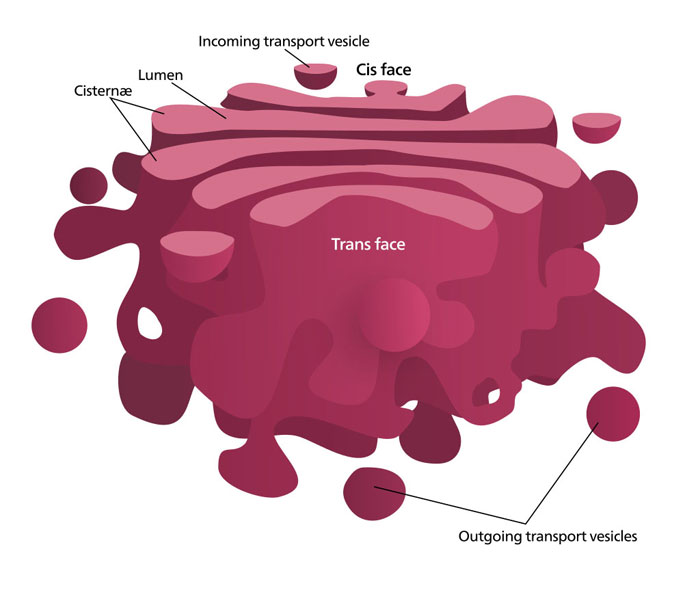
1.10 Golgi apparatus
The golgi apparatus is a stack of smooth cisternae (membrane-bound spaces) piled on each other. These flattened plate-like membrane-bound sacs contain tubules and have vesicles protruding from their margins. Vesicles bud off from the tubules and contain materials for cell wall construction. There is a maturing face and a forming face to the golgi body. New cisternae are added to the forming face and as they mature they move progressively across the stack. At the mature face, cisternae are swollen and secretory vesicles are shed. Once the vesicle detaches from the Golgi body (presumably after reaching a critical size) they move across the cytoplasm to the cell membrane and the material is discharged. The membrane of the vesicle ruptures and becomes continuous with the plasmalemma and the contents are released outside of the cell. Vesicles may also fuse with vacuoles.
Media Attributions
- Figure 1.19.a. Diagram of golgi apparatus showing central membrane bound structure and the vesicles surrounded by a single membrane © Kelvinsong is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
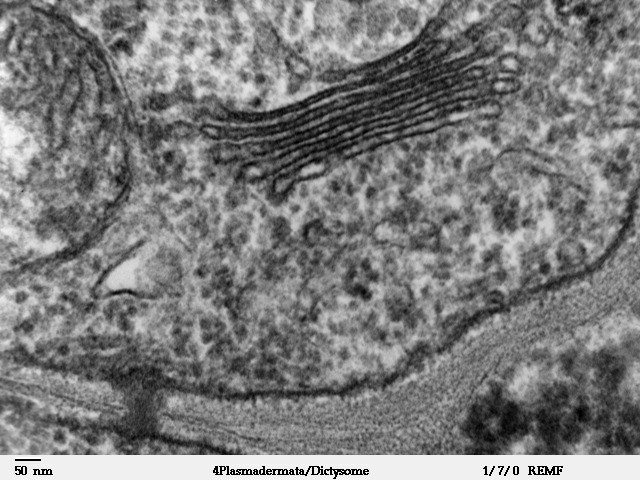
- Figure 1.19.b. Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of golgi apparatus showing central membrane bound structure and the vesicles surrounded by a single membrane. © Louisa Howard, Charles Daghlian is licensed under a Public Domain license

