2.3 Vascular tissues and cell types
There are two vascular tissues in the vascular tissue system: xylem for water transport and phloem for transport of photosynthates.
2.3.1 Xylem
The xylem is a complex tissue containing a range of cell types including: vessel cells, tracheids, fibers, parenchyma
2.3.1.1 Vessel members
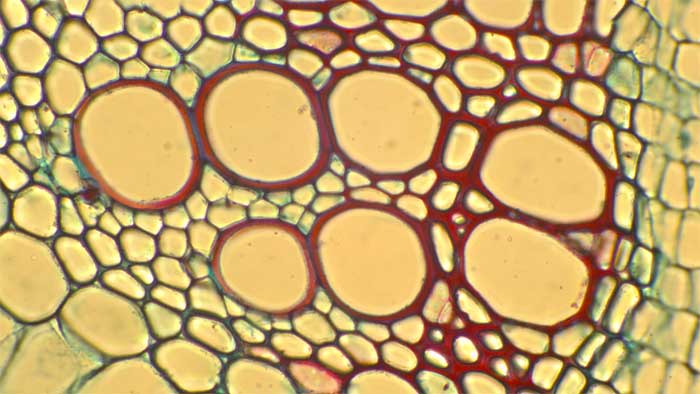
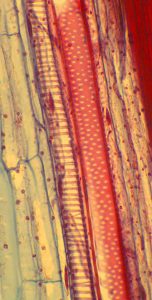
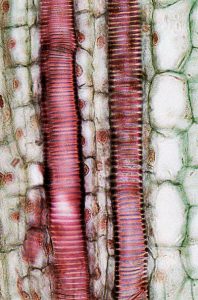

Figure 2.9. Xylem vessel cells with annular lignification in Coleus (left), annular (centre) and reticulate lignification in corn (right).
2.3.1.2 Tracheids
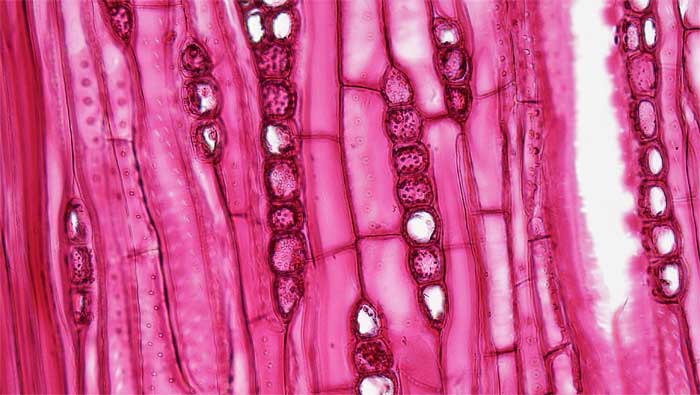
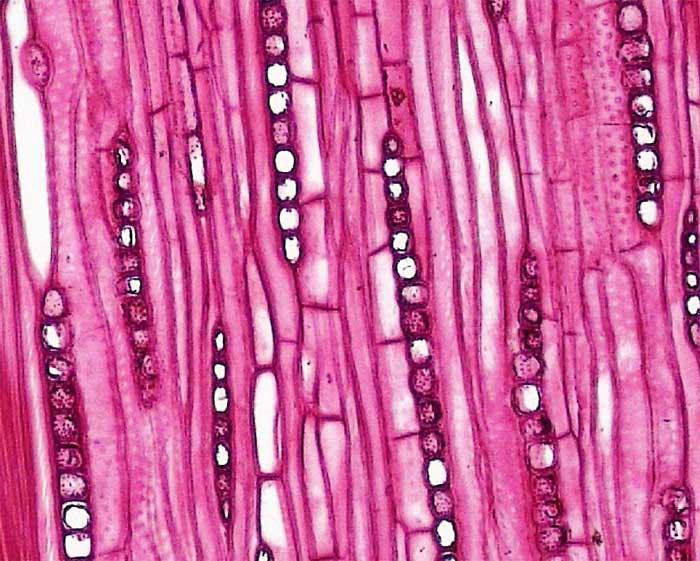
2.3.2 Phloem
2.3.2.1 Sieve cells and companion cells
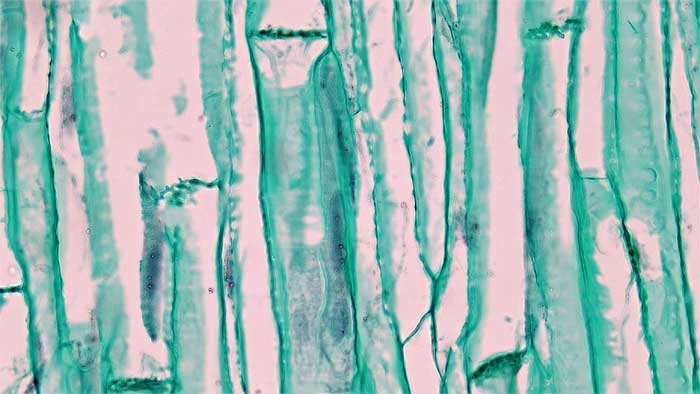
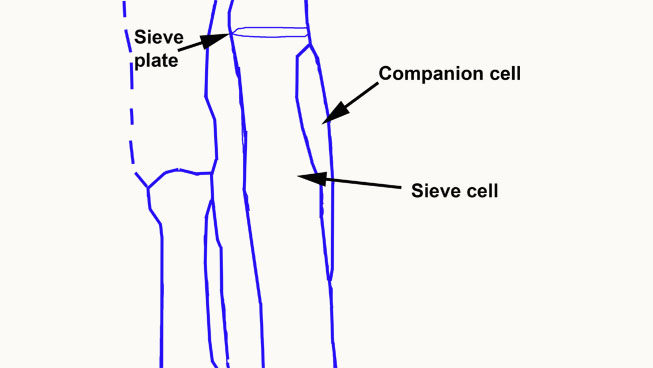
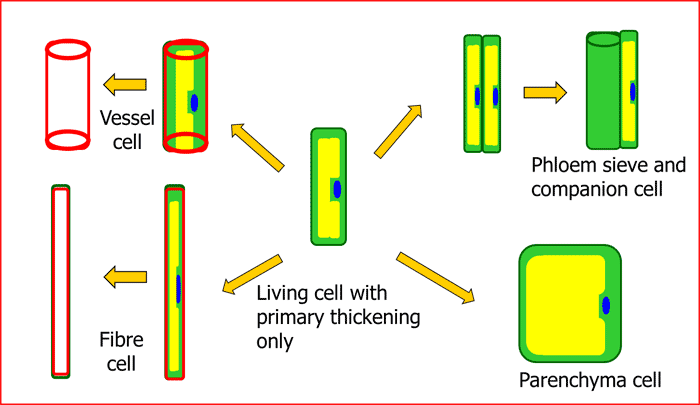
2.3.3 Procambium cell development
Media Attributions
- Figure 2.8. Large xylem vessel cells © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.9.b. Xylem vessel cells © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.9.a. Annular xylem vessels © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.9.c. Zea mays stem © BlueRidgeKitties is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.10.a. Tracheids in tangential section in Quercus © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.10.b. Tracheids in tangential section in Quercus © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.11. Phloem tissue in LS including sieve cells and companion cells © Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Figure 2.12. Diagram shows location of a narrow companion cell alongside a sieve cell and the sieve plate connecting two of the sieve cells © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Figure 2.13. Development of a procambium cell into various vascular tissue cell types © Sean Bellairs is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

